SI (Spark Ignition) and CI (Compression Ignition) engines are two types of internal combustion engines that are commonly used in automobiles. While both types of engines operate on the same basic principle of converting chemical energy into mechanical energy, they differ in how they ignite the fuel-air mixture in the engine's combustion chamber.
Spark Ignition (SI) Engine:
A Spark Ignition engine, also known as a gasoline engine, uses a spark plug to ignite the fuel-air mixture in the combustion chamber. In this type of engine, the fuel and air are mixed together in the carburetor or fuel injector before being drawn into the cylinder. The spark plug then ignites the fuel-air mixture, causing a controlled explosion that pushes the piston down and creates power. The fuel used in SI engines is usually gasoline, but it can also be ethanol or a blend of gasoline and ethanol.
Compression Ignition (CI) Engine:
A Compression Ignition engine, also known as a diesel engine, uses compression to ignite the fuel-air mixture in the combustion chamber. In this type of engine, the air is compressed in the cylinder, causing the temperature to rise. Then, the fuel is injected into the cylinder, and it ignites spontaneously due to the high temperature and pressure. This creates a controlled explosion that pushes the piston down and creates power. The fuel used in CI engines is usually diesel, but it can also be biodiesel or a blend of diesel and biodiesel.
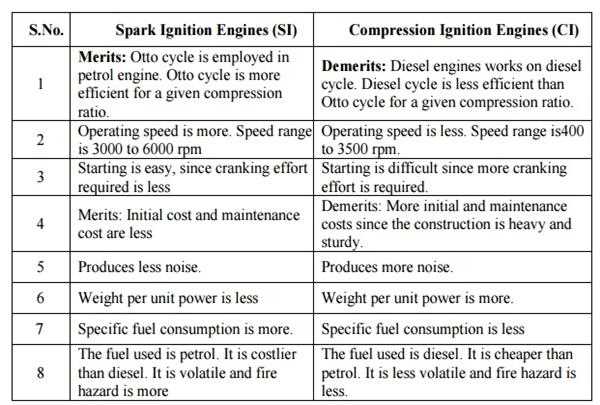
Differences between SI and CI Engines:
Ignition System: The most significant difference between SI and CI engines is the ignition system. SI engines use a spark plug to ignite the fuel-air mixture, while CI engines use compression to ignite the fuel-air mixture.
Fuel Type: SI engines typically use gasoline, while CI engines use diesel fuel. However, SI engines can also run on ethanol or a blend of gasoline and ethanol.
Compression Ratio: CI engines have a higher compression ratio than SI engines. This is because the compression ratio in a CI engine is what causes the fuel to ignite, whereas in an SI engine, the fuel is ignited by a spark plug.
Fuel Efficiency: CI engines are generally more fuel-efficient than SI engines. This is because they operate at a higher compression ratio, which allows them to extract more energy from the fuel.
Emissions: SI engines typically produce more emissions than CI engines, primarily due to incomplete combustion of the fuel-air mixture. CI engines produce fewer emissions due to the high temperature and pressure in the combustion chamber, which allows for more complete combustion.
In conclusion, SI and CI engines differ in their ignition system, fuel type, compression ratio, fuel efficiency, and emissions. Each type of engine has its advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of engine type depends on the specific application and requirements. While SI engines are more common in passenger cars, CI engines are commonly used in commercial vehicles and heavy machinery.