The invention of the generator can be traced back to the early 19th century when scientists and engineers began exploring the concept of electromagnetism. The first practical generator, also known as a dynamo, was invented in 1831 by Michael Faraday.
Faraday discovered that a changing magnetic field within a conductor, such as a wire, would induce an electrical current to flow within the conductor. He demonstrated this principle by building a simple device known as a homopolar generator, which consisted of a wire rotating in a magnetic field. This was the first time that electricity was generated from a mechanical source.
Faraday's work laid the foundation for the development of the generator as we know it today. In the following decades, engineers and inventors improved upon Faraday's design, and by the end of the 19th century, generators had become an essential part of the rapidly growing electrical industry.
Today, generators are used in a wide range of applications, from powering homes and businesses to providing backup power during outages and supplying electricity to remote areas without access to the grid. They have also become an important tool for renewable energy production, such as wind and solar power, by providing a means of storing excess energy when it is generated.
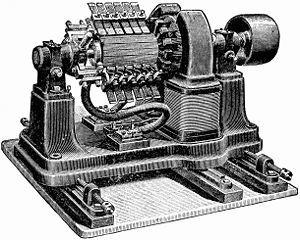
The modern generator is a sophisticated device consisting of a rotating armature, or rotor, within a stationary stator. The rotor is typically powered by an external energy source, such as a steam turbine, internal combustion engine, or wind turbine, and rotates within a magnetic field. This interaction between the magnetic field and the rotor induces an electrical current to flow within the stator, which is then used to power an electrical load.
In conclusion, the invention of the generator was a major milestone in the history of electricity and has profoundly impacted our world. It has made it possible for us to harness electricity's power and has changed how we live, work, and communicate. As we explore new and innovative ways of generating and using electricity, the generator will undoubtedly play a critical role in shaping our energy future.