The ‘Telegraph Code’ was invented by “Samuel Finley Breese Morse” in the year 1816. Famously known as, Samuel Morse. The Telegraph Codes are also known as ‘Morse Code’.

A Telegraph Code is the coding of each Alphabet Character an all the numbers from 0 to 9. All are defined uniquely by using dash (-) and dots (.). These Telegraph Codes are used to transfer information through Telegraphy Machine. These coded information’s are transferred electronically through electrical signals over a wired network between the two stations. In 1844, Morse sends his first Telegraph coded information electrically from Washington, D.C. to Baltimore, Maryland. The speed of sending a message depends upon the size of the message. Usually, the speed of the message is also referred to as words per minute, and is classically based on ‘Paris Formula’. The ‘Paris’ is considered to be as an average length word.
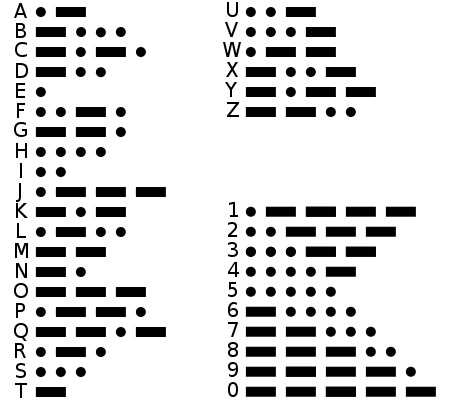
In 1931, the International Code of Signals was originally created to resolve the communication purpose of ships. Later, the demand of Telegraph Code has been declined drastically, as in the 21st Century the Telegraph has been replaced by the Telephone, Fax, and Internet. It became the foundation for the revolution of the communication that led to those later inventions.
The inventor, Samuel Morse, was born in Charlestown, Massachusetts, on April 27, 1791. Morse was a fine painter as well. He completed his graduation in 1810, from Yale College with Phi Beta Kappa honors. In his lifetime, he received various awards. In 1815, he was elected as a Member of the American Antiquarian Society. At Central Park, New York City, a Bronze statue of Samuel Morse has been unveiled on June 10, 1871. The Morse’s Telegraph Code was recognized as an IEEE Milestone in the year 1988. Whereas, he has been also included in the ‘National Inventors Hall of Fame’ in the year 1975.