Indian law aimed at protecting women often reflect a response to historical and social inequalities . The intention is to address gender - based discrimination and violence that woman has faced. While these law aim to empower women , opinion may vary on whether they are balanced or need adjustments to ensure fairness for all.
• In the indian constitution , Article 15 (3) allow the state to make special provisions for women and children. Additionally , Article 39 (a) and Article 42 empazise the state to make provision for securing just and humane condition of work and maternity relief. These provisions highlights the constitutional framework supporting the protection of women's rights in india.
• In Indian penal code (IPC) includes several provisions aims at protecting women. Some relevant sections are
- Section 354:- Deals with assault or criminal forced to woman with intent to outrage her modesty.
- Section 375 and 376:- pertains to rape , defining and penalizing sexual offenses against women.
- Section 498(A):- Addresses cruelty by husband or his relative towards a married woman , often associated with dowry harrassment.
- Section 509:- pertains to words , gesture or act intented to insult the modesty of a woman.
These sections are part of the broader legal framework safeguard women's rights and address crime against them.
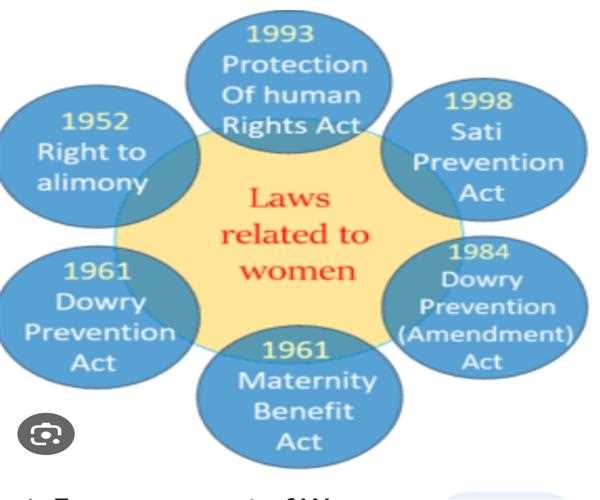
• Indian law provides various provisions to protect women's rights some key legislations includs :-
- Protection of women from domestic violence Act ,2005:- Addresses domestic violence and provide civil remedies for protection orders , residence order etc .
- Sexual harrasment of women at work place Act ,2013:- Mandate the establishment of internal complaints committee to address complaint of sexual harrasment at work place.
- Dowry prohibition Act ,1961:- prohibit the giving or receiving of dowry, aiming to prevent the harassment or cruelty against women related to dowry demand.
- Maternity benefit Act , 1961:- Ensure maternity benefit for women employee,including paid leave and medical benefits.
- Equal remuneration Act, 1976:- Prohibit discrimination in wages on the basis of gender for the same work or work of similar nature. These law collectively contribute to women's protection and empowerment in various aspects of their lives .
Ensuring women safety in India involves a combination of legal provisions and societal change . while law are in place to address and prevent crime against women , the effectiveness of their implementation can vary . Challenge such as underreporting , culture factors and graps in law enforcement may impact the overall safety scenario .
Recent legal intiative ,awareness campaign and increase public discourse highlights a growing emphasis on addressing issues related to women 's safety in India . However sustained efforts in both legal framework and societal attitude are essential to create a safer environment for women.