Recent trends in global economic inequality reveal a complex landscape marked by both progress and challenges. While there have been notable reductions in poverty rates in some regions, a persistent gap between the wealthy and the impoverished persists. The COVID-19 pandemic has exacerbated existing inequalities, disproportionately affecting vulnerable populations and widening the wealth divide.
Technological advancements have played a dual role, contributing to economic growth but also intensifying income inequality. High-skilled workers in tech-centric industries often benefit, while low-skilled workers face displacement. The gig economy's rise has brought flexibility but also job insecurity and limited social protections.
Government policies and taxation systems play a crucial role. Some nations are implementing measures to address inequality, such as progressive taxation and social welfare programs, while others struggle to enact effective policies.
Globalization's impact is evident, with multinational corporations influencing income distribution. Efforts to promote fair trade and ethical business practices aim to mitigate negative effects. Social movements advocating for economic justice and fair wages also shape the discourse, pressuring governments and businesses to address inequality more actively.
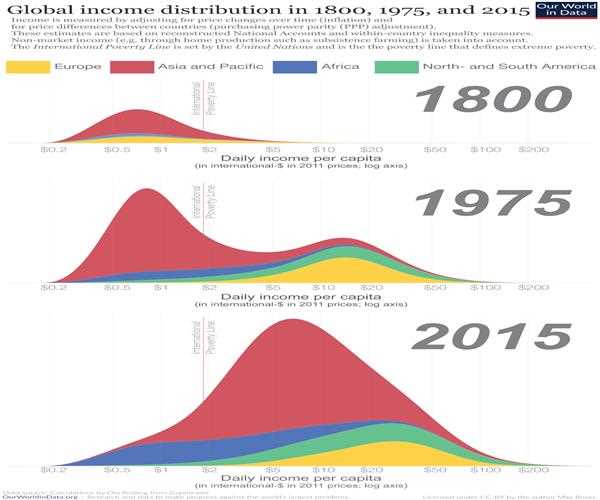
In summary, while there are strides towards addressing global economic inequality, ongoing challenges and new complexities require concerted efforts across sectors to foster a more equitable economic landscape.