- Rig Veda: The Rig Veda is the oldest of the Vedas and is divided into 10 books, or Mandalas. Each Mandala is further divided into hymns, or Suktas. The hymns are addressed to a variety of gods and goddesses, and they praise their power and attributes.
- Yajur Veda: The Yajur Veda is divided into two main parts: the Black Yajur Veda and the White Yajur Veda. The Black Yajur Veda is concerned with the performance of rituals, and it contains mantras, or sacred chants, that are used in these rituals. The White Yajur Veda is a more philosophical text, and it contains discussions of the nature of reality and the goal of human life.
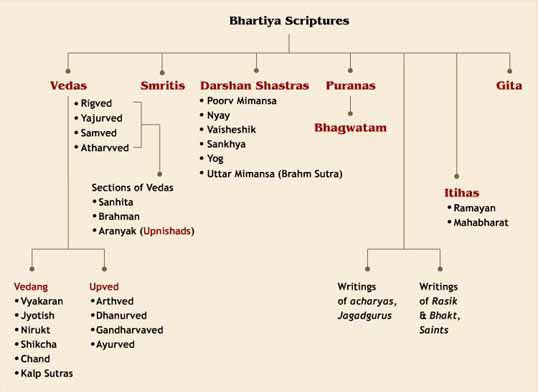
- Sama Veda: The Sama Veda is a collection of hymns that were originally sung during rituals. The hymns are drawn from the Rig Veda, but they have been modified to make them more suitable for singing.
- Atharva Veda: The Atharva Veda is a collection of hymns, spells, and incantations. The hymns are concerned with a variety of topics, including healing, protection, and prosperity.
Each Veda is also divided into four additional layers, or Angas:
- Samhita: The Samhita is the oldest layer of the Vedas, and it contains the core texts of each Veda.
- Brahmana: The Brahmana is a layer of commentary on the Samhitas. It contains explanations of the rituals and sacrifices that are described in the Samhitas.
- Aranyaka: The Aranyaka is a layer of philosophical and mystical texts. It contains discussions of the nature of reality, the goal of human life, and the nature of the gods.
- Upanishad: The Upanishads are the most recent layer of the Vedas. They are a collection of philosophical texts that discuss the nature of Brahman, the soul, and the relationship between the two.
The Vedas are a vast and complex body of literature, and their division into different parts reflects the different purposes that they served in ancient India. The Samhitas were used for ritual purposes, the Brahmanas were used for instruction, the Aranyakas were used for meditation, and the Upanishads were used for philosophical contemplation.