The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the network of physical objects, devices, vehicles, and other items embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity capabilities that enable them to collect and exchange data over the internet. These interconnected devices can communicate with each other, as well as with humans, to provide valuable information, automate processes, and facilitate decision-making.
The IoT enables the interconnection of physical devices through a combination of hardware, software, and networking technologies. At its core, IoT relies on sensors and actuators that gather data from the physical world and perform actions in response to that data. These devices are equipped with various types of sensors, such as temperature sensors, motion sensors, or GPS receivers, which collect data about their environment.
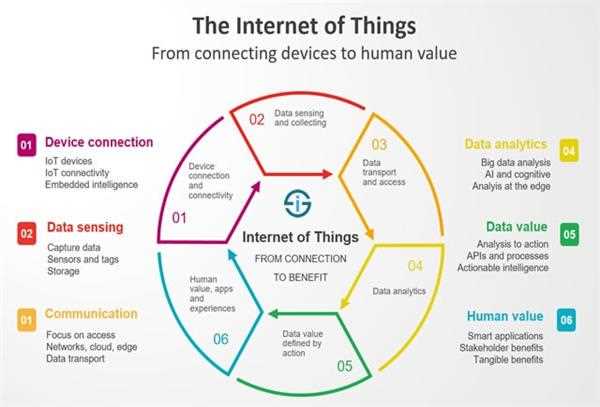
The collected data is then processed and transmitted to the cloud or local servers using wired or wireless communication technologies, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or cellular networks. Once the data is in the cloud, it can be analyzed and combined with other data sources to derive insights and trigger actions.
The interconnection of physical devices in IoT creates a vast network of information, allowing for real-time monitoring, control, and optimization of processes across different domains, including smart homes, industrial automation, healthcare, transportation, and more. For example, in a smart home scenario, IoT devices like thermostats, lights, and security cameras can communicate with each other to create an intelligent environment that adjusts settings based on occupancy, weather conditions, or user preferences.
Overall, the IoT's ability to interconnect physical devices enhances efficiency, improves decision-making, and opens up new possibilities for automation and innovation across various industries and everyday life.