Databases and spreadsheets are both used for storing and manipulating data, but they have some key differences in their design, functionality, and intended use.
A database is a collection of data that is organized in a specific way to facilitate efficient data storage, retrieval, and management. Databases typically use a structured data model, such as a relational or NoSQL data model, to define the relationships between different types of data. They are designed to handle large amounts of data and support complex queries and operations.
A spreadsheet, on the other hand, is a tool for organizing and manipulating data in a tabular format. Spreadsheets are typically used for smaller, simpler datasets and are not as well-suited for handling large amounts of data or complex operations. They are also less flexible in terms of data organization, as they are limited to a single table format.
One of the key differences between databases and spreadsheets is their approach to data storage and organization. Databases are designed to store data in a structured format, with each piece of data stored in a specific field or column within a table.
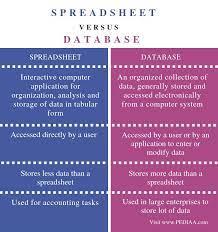
This allows for efficient data retrieval and manipulation, as queries can be executed against specific fields or groups of fields. Spreadsheets, on the other hand, store data in a flat table format, with each row representing a unique record and each column representing a specific data field. While this format is simple and easy to use for small datasets, it can become unwieldy and difficult to manage as the dataset grows in size and complexity.
Another key difference between databases and spreadsheets is their support for concurrent access and data sharing. Databases are designed to handle multiple users accessing and modifying data simultaneously, with built-in mechanisms for ensuring data consistency and integrity. Spreadsheets, on the other hand, are typically designed for single-user access and do not support concurrent access or data sharing.
In terms of functionality, databases offer a wide range of features and capabilities for managing and manipulating data. These include support for complex queries and operations, data validation and normalization, data security and access control, and data backup and recovery. Spreadsheets, on the other hand, offer more basic data manipulation and analysis tools, such as sorting, filtering, and simple formulas.
Finally, databases and spreadsheets are designed for different use cases. Databases are typically used for managing large amounts of data in an organized, efficient, and secure manner. They are commonly used in business, finance, healthcare, and other industries where data management is critical. Spreadsheets, on the other hand, are more commonly used for small-scale data manipulation and analysis, such as budgeting, inventory tracking, and simple data visualization.
In conclusion, while both databases and spreadsheets are used for storing and manipulating data, they have some key differences in their design, functionality, and intended use. Databases are designed for managing large amounts of structured data, supporting complex queries and operations, and handling concurrent access and data sharing. Spreadsheets, on the other hand, are designed for simple data manipulation and analysis and are not as well-suited for handling large amounts of data or complex operations. By understanding these differences, users can choose the tool that best fits their needs and requirements.
