In SQL Server, a JOIN operation combines rows from two or more tables based on a related column between them. A JOIN clause is used to specify the relationship between the tables being joined.
There are four main types of JOINs in SQL Server:
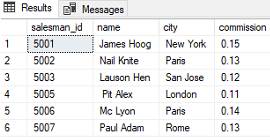
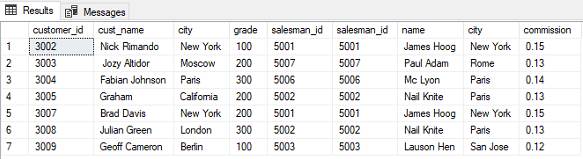
- Inner Join: Returns only the rows that have matching values in both tables being joined.
- Left Outer Join: Returns all the rows from the left table and matching rows from the right table. If there is no matching row in the right table, the result will contain NULL values.
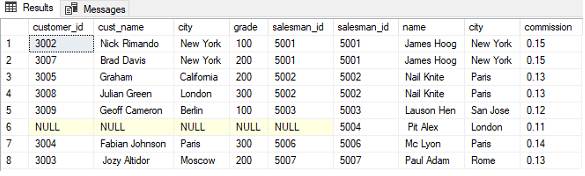
- Right Outer Join: Returns all the rows from the right table and matching rows from the left table. If there is no matching row in the left table, the result will contain NULL values.
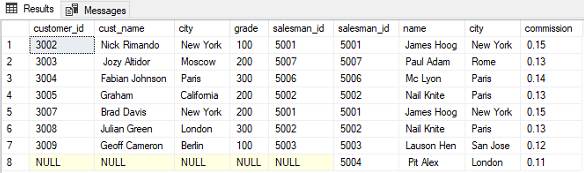
- Full Outer Join: Returns all the rows from both tables, including any rows that do not have matching values in the other table. If there is no matching row in one of the tables, the result will contain NULL values.
Each type of JOIN has its own syntax and usage, and it's important to choose the right type of JOIN for the specific task at hand.
Suppose you have two tables: "employees" and "departments". The "employees" table has columns for employee ID, name, and department ID. The "departments" table has columns for department ID and department name.
To join these two tables based on the department ID column, you can use an INNER JOIN like this:
SELECT employees.name, departments.department_name
FROM employees
INNER JOIN departments
ON employees.department_id = departments.department_id;This SQL query will return a result set that includes the names of all employees and their corresponding department names. The INNER JOIN operation ensures that only the rows that have matching department IDs in both tables are included in the result set.
You can use other types of JOINs in a similar manner, by replacing "INNER JOIN" with "LEFT OUTER JOIN", "RIGHT OUTER JOIN", or "FULL OUTER JOIN" depending on the specific requirements of your query.