Overview
Lower back pain could be a common cause for visits to the doctor.
According to the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS), lower back pain is the most common cause of job-related disability. At least 80 percent of usa citizens will experience lower back pain in their lifetime.
Most lower back pain is that the results of an injury, like muscle sprains or strains because of sudden movements or poor body mechanics while lifting heavy objects.
Lower back pain also can be the results of certain diseases, such as:
- Cancer of the spinal cord
- A ruptured or herniated disc
- Sciatica
- Arthritis
- Kidney infections
- Infections of the spine
Acute back pain can last anywhere from a number of days to a number of weeks, while chronic back pain is pain that lasts longer than three months.
Lower back pain is more likely to occur in individuals between the ages of 30 and 50. This is partly due to the changes that occur in the body with aging. As you get older , there‘s a discount within the fluid content between the vertebrae within the spine.
This means discs within the spine experience irritation more easily. You also lose some muscular tonus , which makes the rear more susceptible to injury. This is why strengthening your back muscles and using good body mechanics are helpful in preventing lower back pain.
What are the causes of lower back pain?
Strains
The muscles and ligaments within the back can stretch or tear because of excess activity. Symptoms include pain and stiffness within the lower back, also as muscle spasms. Rest and physiotherapy are remedies for these symptoms.
Disc injury
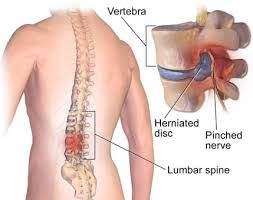
The discs within the back are susceptible to injury. This risk increases with age. The outside of the disc can tear or herniate.
A ruptured intervertebral disc , which is additionally referred to as a slipped or ruptured disc, occurs when the
cartilage surrounding the disc pushes against the medulla spinalis or nerve roots. A cushion between the spinal vertebrae extends outside its normal position.
This can end in compression of the nerve root because it exits from the medulla spinalis and through the vertebral bones. Disc injury usually occurs suddenly after lifting something or twisting the rear . Unlike a back strain, pain from a disc injury usually lasts for quite 72 hours.
Sciatica
Sciatica can occur with a herniated disc if the disc presses on the sciatic nerve. The nervus ischiadicus connects the spine to the legs. As a result, sciatica can cause pain within the legs and feet. This pain usually seems like burning, or pins and needles.
Spinal stenosis
Spinal stenosis is when the vertebral column narrows, putting pressure on the medulla spinalis and spinal nerves.
Spinal stenosis is most commonly due to degeneration of the discs between the vertebrae. The result's compression of the nerve roots or medulla spinalis by bony spurs or soft tissues, like discs.
Pressure on the spinal nerves causes symptoms such as:
- Numbness
- Cramping
- Weakness
You might feel these symptoms anywhere within the body. Many people with spinal stenosis notice their symptoms worsen when standing or walking.
Abnormal spine curvatures
Scoliosis, kyphosis, and lordosis are all conditions that cause abnormal curvatures in the spine.
These are congenital conditions that are usually first diagnosed during childhood or adolescence. The uncommon curvature causes pain and poor posture because it places pressure on:
- Muscles
- Tendons
- Ligaments
- Vertebrae
Other conditions
There are variety of other conditions that cause lower back pain. These conditions include:
- Arthritis is an inflammation of the joints.
- Fibromyalgia is long-term pain and tenderness in the joints, muscles, and tendons.
- Spondylitis is inflammation of the joints between the spinal bones.
- Osteochondritis is a degenerative disorder that may cause loss of normal spinal structure and function. Although aging is that the primary explanation for the condition, the situation and rate of degeneration is restricted to the individual.
Some more health conditions that can cause lower back pain include:
Kidney and bladder problems
- Pregnancy
- Endometriosis
- Ovarian cysts
- Uterine fibroids
- Cancer
How is lower back pain diagnosed?
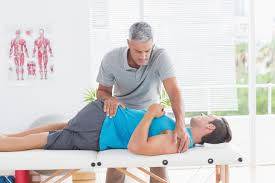
Your doctor will likely begin by requesting a complete medical history and conducting a thorough physical examination to determine where you‘re feeling the pain. A physical exam also can determine if pain affects your range of motion.
Your doctor may also check your reflexes and your responses to certain sensations. This determines if your lower back pain affects your nerves.
Unless you have concerning or debilitating symptoms or neurologic loss, your doctor will probably monitor your condition for a few weeks before sending you for testing. This is because most lower back pain resolves using simple self-care treatments.
Certain symptoms require more testing, including:
- Lack of bowel control
- Weakness
- Fever
- Weight loss
Likewise, if your low back pain continues after home treatment, your doctor might want to order additional tests.
Seek medical attention immediately if you experience any of those symptoms additionally to lower back pain.
Imaging tests such as X-rays, CT scans, ultrasounds, and MRIs may be necessary so your doctor can check for:
- Bone problems
- Disc problems
- Problems with the ligaments and tendons in your back
If your doctor suspects a problem with the strength of the bones in your back, they may order a bone scan or bone density test. Electromyography (EMG) or nerve conduction tests can help identify any problems with your nerves.
What are the medicaments options for lower back pain?

Home care
Self-care methods are helpful for the first 72 hours after the pain begins. If the pain doesn’t improve after 72 hours of home treatment, you must call your doctor.
Stop your normal physical activities for a few of days and apply ice to your lower back. Doctors generally recommend using ice for the primary 48 to 72 hours, then switching to heat.
Alternate ice and heat to relax muscles. The RICE protocol — rest, ice, compression, and elevation — is suggested within the primary 48 hours.
Take over-the-counter pain medication, such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB), or acetaminophen (Tylenol), to relieve pain.
Sometimes lying on your back causes more discomfort. If so, try lying on your side with your knees bent and a pillow between your legs. If you can lie comfortably on your back, place a pillow or rolled-up towel beneath your thighs to reduce the pressure on the lower back.
A warm bath or a massage can often relax stiff and knotted muscles within the back.
Medical treatment
Low back pain can occur with variety of various conditions, including:
- muscle strain and weakness
- pinched nerves
- spinal cord misalignment
There are variety of possible medical treatments including:
- medications
- medical appliances
- physical therapy
Your doctor will determine the acceptable dosage and application of medicine and medications supported your symptoms.
Some medications your doctor may prescribe include:
- muscle relaxants
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- narcotic drugs such as codeine for pain relief
- steroids to reduce inflammation
- corticosteroid injections
Your doctor may also prescribe physical therapy, including:
- massage
- stretching
- strengthening exercises
- back and spinal manipulation
Surgery
For severe cases, surgery may be necessary. Surgery is typically only an option when all other treatments fail. However, if there’s loss of bowel or bladder control, or a progressive neurological loss, surgery becomes an emergency option.
A discectomy relieves pressure from a nerve root pressed on by a bulging disc or bone spur. Surgeon will remove a small piece of the lamina, a bony a part of the vertebral canal .
A foraminotomy may be a surgery that exposes the foramen, the bony hole within the spinal canal where the nerve root exits.
There is a therapy also named Intradiscal electrothermal therapy (IDET) it involves inserting a needle through a catheter into the disc and heating it up for 20 minutes. This makes the disc wall thicker and cuts down on the inner disc’s bulging and irritation of the nerve.
A spinal laminectomy, also known as spinal decompression, removes the lamina to make the size of the spinal canal bigger. This relieves pressure on the spinal cord and nerves.
How can I prevent low back pain?
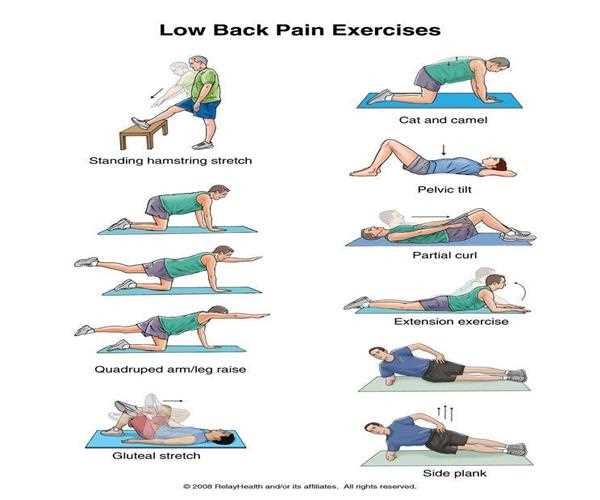
There are some ways to stop low back pain. Practicing prevention techniques can also help lessen the severity of your symptoms if you've got a lower back injury.
Prevention involves:
- exercising the muscles in your abdomen and back
- losing weight if you’re overweight
- lifting items properly by bending at the knees and lifting with the legs
- maintaining proper posture
You may also want to:
- sleep on a firm surface
- sit on supportive chairs that are at the correct height
- avoid high-heeled shoes
- quit smoking, if you smoke
Nicotine causes degeneration of spinal discs and also reduces blood flow.
Call your doctor and tell him/her about your lower back pain. They can diagnose the cause and help you create a treatment plan that works best for you.