Answer - option (d)
The Electro-Magnetic or EM radiation is classified into types according to the frequency of the wave: these types include, in order of increasing frequency, radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays and gamma rays.
| Category |
Range of Wavelengths (nm) |
Range of Frequencies (Hz) |
| Gamma rays |
<1<1 |
>3×1017>3×1017 |
| X-rays |
1–101–10 |
3×1016–3×10173×1016–3×1017 |
| Ultraviolet light |
10–40010–400 |
7,5×1014–3×10167,5×1014–3×1016 |
| Visible light |
400–700400–700 |
4,3×1014–7,5×10144,3×1014–7,5×1014 |
| Infrared |
700–105700–105 |
3×1012–4,3×10143×1012–4,3×1014 |
| Microwave |
105–108105–108 |
3×109–3×10123×109–3×1012 |
| Radio waves | >108>108 | <3×109 |
These are some examples of uses of electromagnetic waves :
| Category |
Uses |
| gamma rays |
used to kill the bacteria in marshmallows and to sterilize medical equipment |
| X-rays |
used to image bone structures |
| ultraviolet light |
bees can see into the ultraviolet because flowers stand out more clearly at this frequency
|
| visible light |
used by humans to observe the world |
| infrared |
night vision, heat sensors, laser metal cutting |
| microwave |
microwave ovens, radar |
| radio waves | radio, television broadcasts |
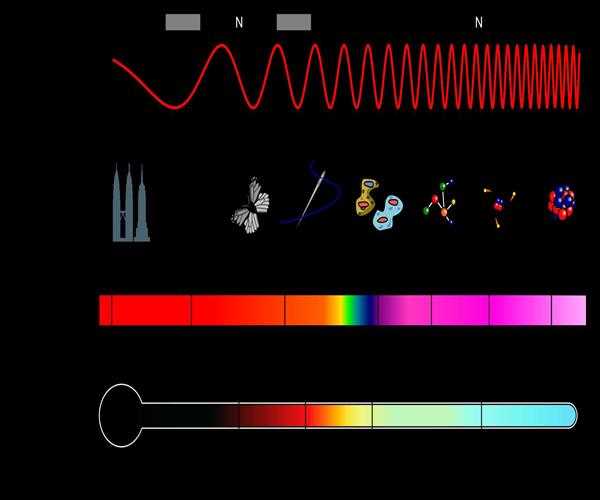
image source from Wikipedia