
The R.B.I. or the Reserve Bank of India is country’s central banking institution. It controls the monetary policy of the Indian currency. It was established on 1 April 1935 under the British Empire as per the provisions of the Reserve Bank of India Act, passed in 1934. The bank was initially owned entirely by private shareholders but after India's independence on 15 of August in 1947, the Reserve Bank of India was completely nationalized on 1st January, 1949.
In the early days, the Central Office of the Reserve Bank was established in Calcutta. However, later it was permanently moved to Mumbai in 1937. The Central Office is where the Governor sits. Also, all the policies regarding money & bank regulations are formulated here.

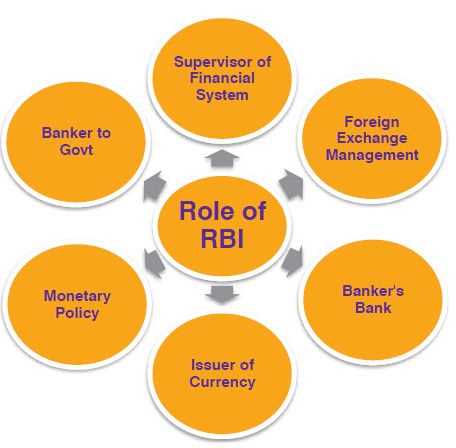
Owning to the fact that it controls the entire country’s monetary flow, the Reserve Bank of India plays a very vital role in the formulation of strategies for the development of the Indian Government. It controls & regulates the entire banking system of the nation & ensures the monetary stability for the citizens of this country. It is also responsible for printing the currency notes & operating the entire nation’s credit and currency system. From its position at the top of the banking system pyramid, the Reserve Bank of India is thus, at the center of economic system of the country.
The logo of the Reserve Bank of India was inspired from the East India Company’s “Double Mohur”. The bank’s financial year spans from 1st of July to 30th of June. Though, RBI is responsible only for printing the currency notes...minting of coins is done by the Government of India. Also, an interesting fact about the Reserve Bank of India is that it also used to be the central bank for two other countries, Pakistan & Myanmar. It acted as the Central Bank of Pakistan till June of 1948 and the Central Bank of Burma (Myanmar) till April of 1947.
