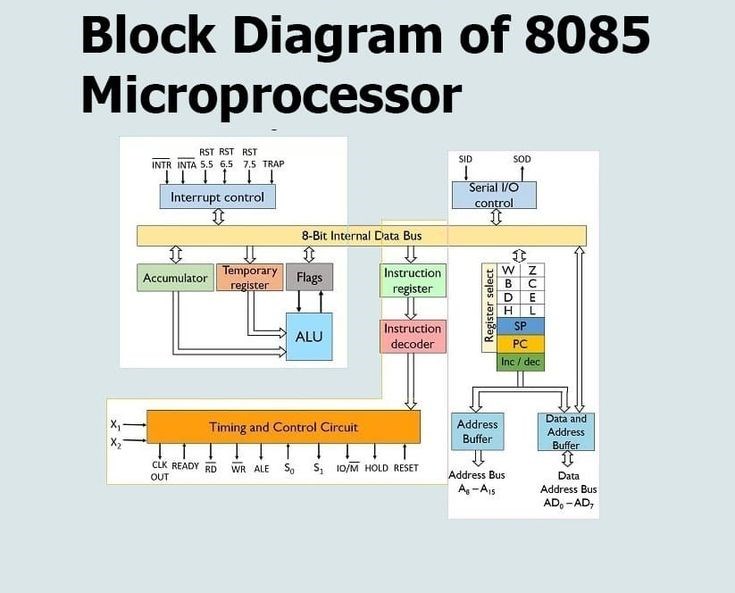
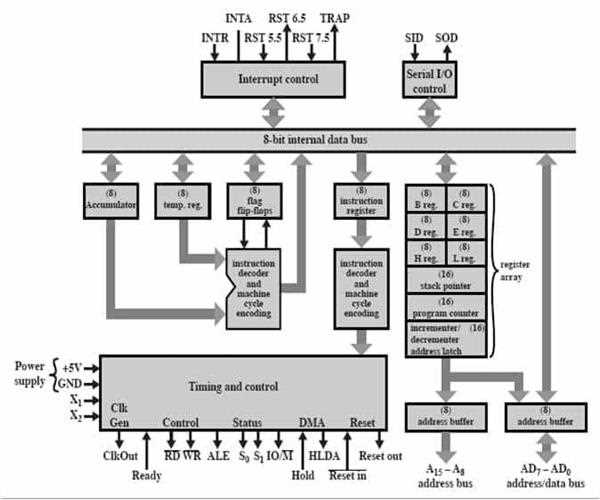
The 8085 processor is called an 8-bit processor because its data bus can only transfer 8 bits of data at a time, meaning it can process information in units of 8 binary digits simultaneously; essentially, all its internal registers and operations are designed to handle data in 8-bit chunks.
Key points about the 8085 processor:
Data bus width:
The primary reason for calling it an 8-bit processor is that its data bus is 8 bits wide.
Register size:
All the general-purpose registers within the 8085 can store 8 bits of data.
Arithmetic operations:
The arithmetic logic unit (ALU) in the 8085 is also designed to perform calculations on 8-bit data.