Search Method Holding On Less Memory!

Depth-First Search is the traversal technique that occupies less space in memory. Well, this is fine if it takes less memory space but exactly it is… that is a question!
Depth First Search (DFS):
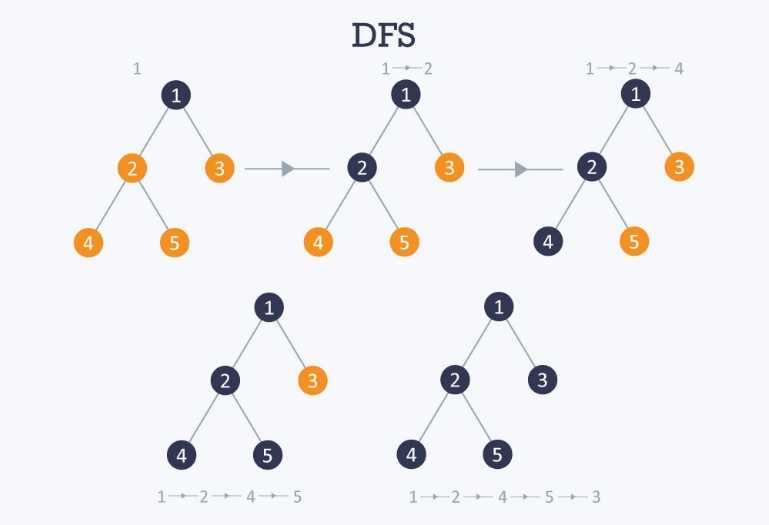
It is an algorithm which is recursive in nature and uses the idea of backtracking. It involves all the possible searches that maybe exhaustive as it traverses through all the nodes and if required then it backtrack also.
Now, a new term is been tossed “Backtrack”, thus it can be explained as while traversing through the nodes, if we encounter with a node that is a child node, it steps backward from that node to find the next path that can be traversed. All the nodes would be visited on the current path, till the time every unvisited node is not been traversed, after that only can a next path be chosen.
Stating about its functionality, DFS can be implemented using stacks, which can be shown in the below code:
- Pivot the starting node and stack the rest of the adjacent nodes in the stack
- Pop a node from the stack to select the next node to traverse and Push all its adjacent nodes into the stack
- Continue, repeating this until the stack is empty. However, a mark is been made if the node is been visited wherein, this function would prevent you from visiting the same node again and again and if not then may you end up in the condition of infinite loop
Pseudocode:
DFS (G, s): //Where G is graph and s is source vertex
Let A be stack
A.push(s) //Inserting s in stack
mark A as visited.
while (A is not empty):
//Pop a vertex from stack to visit next
b = A.top( )
A.pop ( )
//Push all the neighbors of v in stack that are not visited
for all neighbors c of b in Graph G:
if c is not visited :
A.push(c)
mark c as visited
DFS-recursive (G, s):
mark s as visited
for all neighbors c of s in Graph G:
if c is not visited:
DFS-recursive (G, c)
Hope this would help you to get the info about DFS!
Cheers!