Smart home devices communicate through various wireless protocols that enable seamless connectivity and interoperability. Common communication technologies include Wi-Fi, Zigbee, Z-Wave, and Bluetooth. Wi-Fi is prevalent for high-bandwidth applications, allowing devices to connect to a home network and the internet, facilitating remote control and monitoring.
Zigbee and Z-Wave are wireless mesh networks designed specifically for smart home applications. Zigbee operates on low power and is suitable for devices that need to conserve energy, while Z-Wave excels in reliability and low interference, making it suitable for home automation. These mesh networks allow devices to form a decentralized communication network, enhancing coverage and reliability by passing data through multiple nodes.
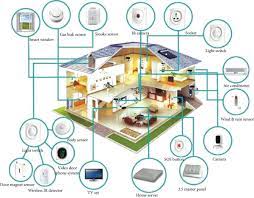
Bluetooth, with its low energy variant (Bluetooth Low Energy or BLE), is commonly used for short-range communication between devices. It is ideal for connecting smartphones, tablets, and wearables to smart home devices.
Interoperability remains a challenge, as devices from different manufacturers may use different communication protocols. Efforts like the Zigbee Alliance's Project Connected Home over IP (CHIP) aim to standardize smart home device communication, promoting cross-compatibility and a more cohesive smart home ecosystem.