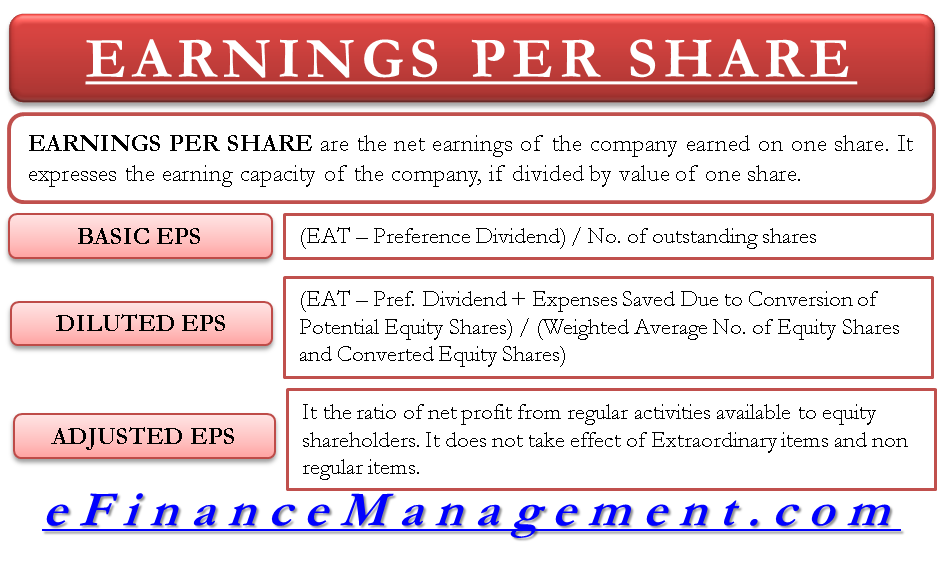
Earnings Per Share (EPS) is determined by separating an organization's net income by the quantity of remarkable offers, addressing the part of benefit distributed to each share.
- Productivity Marker:
EPS is a crucial proportion of an organization's benefit. It mirrors the income produced for each extraordinary portion of normal stock. Higher EPS values demonstrate more ground-breaking productivity.
- Financial Backer Navigation:
Financial backers frequently use EPS as a basic component while making venture choices. It influences stock valuation and the attractiveness of investments by assisting in the evaluation of a company's financial health and performance.
- Relative Examination:
EPS considers the correlation of productivity across various organizations and ventures. A normalized measurement works with the evaluation of relative monetary execution.
- Profit Patterns:
Following changes in an organization's EPS over the long haul uncovers profit patterns. Reliable development in EPS might show powerful administration and a positive direction for the organization.
- Profit Payouts:
Organizations with positive EPS frequently utilize a piece of their profits to deliver profits to investors. Financial backers looking for money are especially keen on EPS as it relates to potential profit payouts.
- Monetary Estimating:
EPS is a vital part of monetary estimation. Examiners use past EPS information and other monetary measurements to make projections about an organization's future profit and, by and large, monetary execution.
- Share Value Effect:
The stock price of a company can be significantly affected by changes in EPS.
- Profit Quality:
A company's earnings quality can be gauged by analyzing EPS. Economical and predictable EPS development demonstrates a powerful monetary establishment, while unpredictable or whimsical EPS might raise concerns.
- Management Decision Support System:
Organizational executives likewise involve EPS as a device to assess monetary procedures and functional choices. Maximizing EPS is frequently a goal, but not at the expense of sustainability in the long run.
- Effects of Offer Buybacks:
Organizations participating in share buyback projects can emphatically impact EPS. As the quantity of extraordinary offers diminishes, EPS will in general ascent, possibly flagging upgraded investor esteem.
In synopsis, Profit Per Offer is a vital monetary metric that assumes a critical part in assessing an organization's monetary exhibition, helping financial backers, experts, and the executives in coming to informed conclusions about venture, monetary methodology, and generally speaking business wellbeing.
Read more: What are the benefits of using a systematic investment plan (SIP)