The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) reference model is a conceptual framework that describes the functions of a network communication system. It was developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) in the 1980s to provide a standard way to describe network protocols and facilitate interoperability between different network technologies. The OSI reference model has seven layers, which are: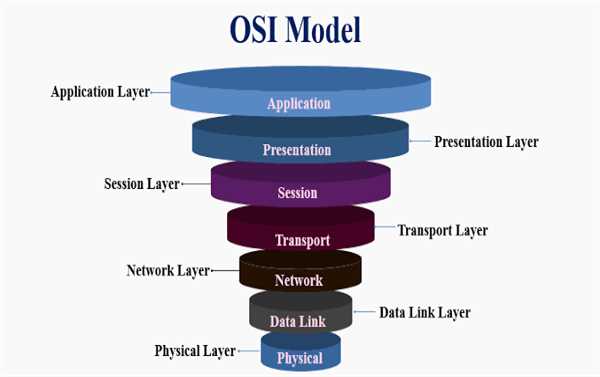
- Physical Layer: The physical layer is responsible for transmitting raw bits over a physical medium, such as copper wires or fiber optic cables. It defines the electrical, mechanical, and timing specifications for the physical medium and the interface between the medium and the devices on the network.
- Data Link Layer: The data link layer is responsible for transmitting data between adjacent nodes on a network. It is divided into two sublayers: the LLC (Logical Link Control) sublayer and the MAC (Media Access Control) sublayer. The LLC sublayer provides flow control and error checking, while the MAC sublayer provides addressing and access control.
- Network Layer: The network layer is responsible for transmitting data between nodes that are not directly connected. It provides routing and addressing services, allowing data to be transmitted across multiple network segments. The network layer is where the IP (Internet Protocol) protocol resides.
- Transport Layer: The transport layer is responsible for providing reliable end-to-end communication between applications. The transport layer protocols, such as TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and UDP (User Datagram Protocol), are commonly utilized to guarantee the accurate delivery of data without any errors and in the correct sequence.
- Session Layer: The session layer is responsible for establishing, maintaining, and terminating sessions between applications. It provides services such as authentication and encryption, allowing applications to communicate securely over the network.
- Presentation Layer: The presentation layer is responsible for translating data between the application format and the network format. It provides services such as data compression and encryption, allowing applications to exchange data in a format that is compatible with the network.
- Application Layer: The OSI model's uppermost layer is referred to as the application layer. It provides services that are used by applications to communicate with each other over the network. Examples of application layer protocols are HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol), FTP (File Transfer Protocol), and SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol).
The OSI reference model is a theoretical framework that provides a standard way to describe network protocols and facilitate interoperability between different network technologies. While most modern networks do not strictly adhere to the OSI model, it remains a useful tool for understanding network protocols and their interactions.